Webpack Basics
Webpack is a JS module bundler, module dependency manager that takes the dependency tree and creates one or more resulting files containing the entire project codebase. It manages the order of adding modules and also bundles, minifies, packs, and much more.
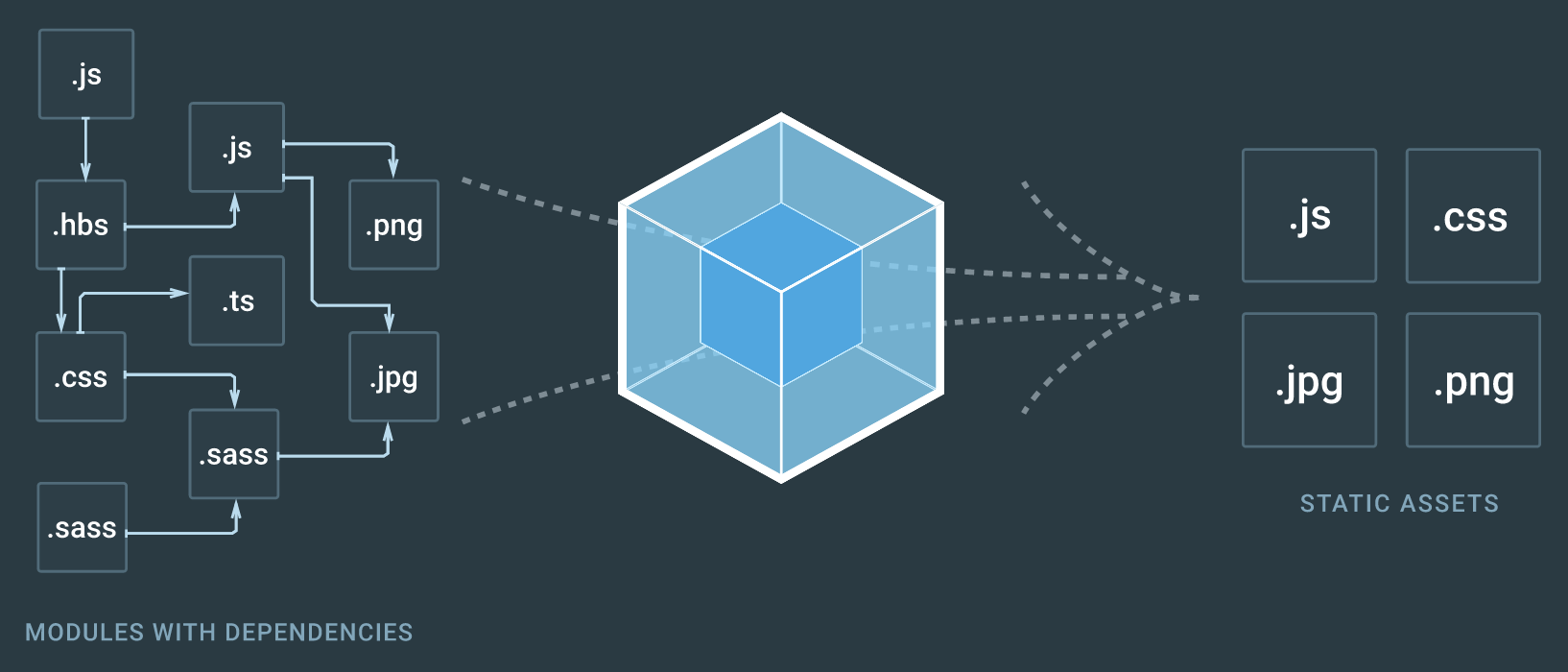
Webpack has become one of the most important web developer tools. First of all, it is an application module dependency manager and a JS file bundler, but it can transform all resources (HTML and CSS, SASS, etc.), optimize images, compile templates, run a local web server for development purposes, and much more.
How it works
Let's say you have an application that can do two simple mathematical operations, addition and multiplication. You split these functions into separate files (modules) to simplify your codebase maintenance. Then scripts will be added to index.html in the following order.
<script src="sum.js"></script>
<script src="multiply.js"></script>
<script src="index.js"></script>
Suppose the code from sum.js is used in multiply.js and index.js, and the code from multiply.js is used only in index.js. Let's see the hierarchy of dependencies in a simple diagram.
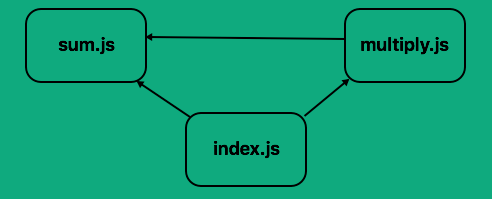
If you make a mistake in the sequence of adding scripts to index.html, that is, if index.js is added before any other dependencies, or if sum.js is added after multiply.js, there will be errors. Now, imagine you scale this to a real, full-scale application with hundreds of dependencies. Maintaining the order of adding scripts would be a nightmare.
Webpack converts dependencies into modules and bundles them into one or more files. Each module will have a private namespace and correct order.
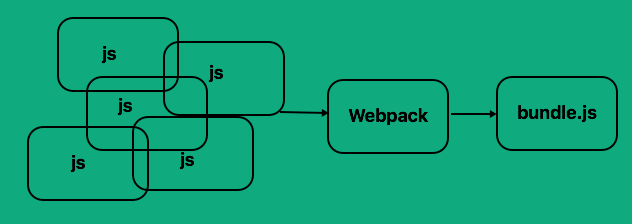
Gulp still occupies its rightful place in the developer toolkit, and for some projects, Webpack is not needed, although they can co-exist. However, despite that the learning curve can be higher with more complex settings. Webpack is indispensable if you use present-day libraries and frameworks for development such as React, Vue, Angular, etc.
Setting up
Follow the links below for comprehensive, step-by-step tutorials explaining how to set up Webpack.