Arrays
Array is a data structure for storing and manipulating collections of indexed values. Arrays are used to store ordered data collections such as a list of resorts, products, hotel guests, etc.
Creation
An array is declared with the opening and closing square brackets [], array
literals. Inside the brackets, each array element is separated by a comma.
const clients = ["Mango", "Poly", "Ajax"];
Access to elements
To access the values of array elements, use syntax with square brackets,
array[index]. There should be no space between the name of the variable
storing the array and the brackets.
const clients = ["Mango", "Poly", "Ajax"];
// By specifying the element index in brackets, you get its value
console.log(clients[0]); // Mango
console.log(clients[1]); // Poly
console.log(clients[2]); // Ajax
Array elements are indexed starting at zero.
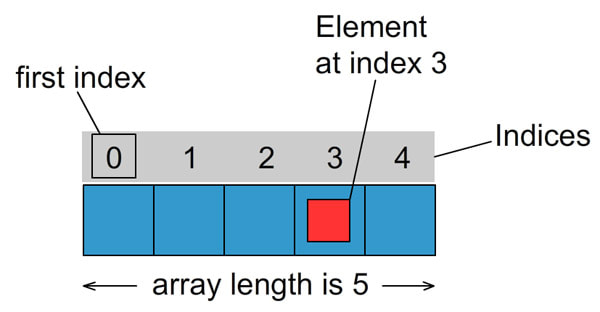
Overriding
Unlike strings, array elements can be changed if you access them by index and assign a different value.
const clients = ["Mango", "Poly", "Ajax"];
clients[0] = "Kiwi";
clients[1] = "Pango";
console.log(clients); // ["Kiwi", "Pango", "Ajax"]
Array length
The length of an array, that is, the number of its elements, is stored in the
length property. It is a dynamic value that changes automatically when
elements are added or removed.
const clients = ["Mango", "Poly", "Ajax"];
console.log(clients.length); // 3
Last element's index
Most often, we do not know in advance the length of an array. In order to get
the value of the last element, use the following approach: the array length is
always the index of the last element + 1. Using the formula array_length - 1,
you can get the value of the last element of any array with arbitrary length.
const clients = ["Mango", "Poly", "Ajax"];
const lastElementIndex = clients.length - 1;
console.log(lastElementIndex); // 2
console.log(clients[lastElementIndex]); // "Ajax"