Document Object Mode
The functionality for work with a browser consists of several modules, since JavaScript does not have tools for working with browsers.
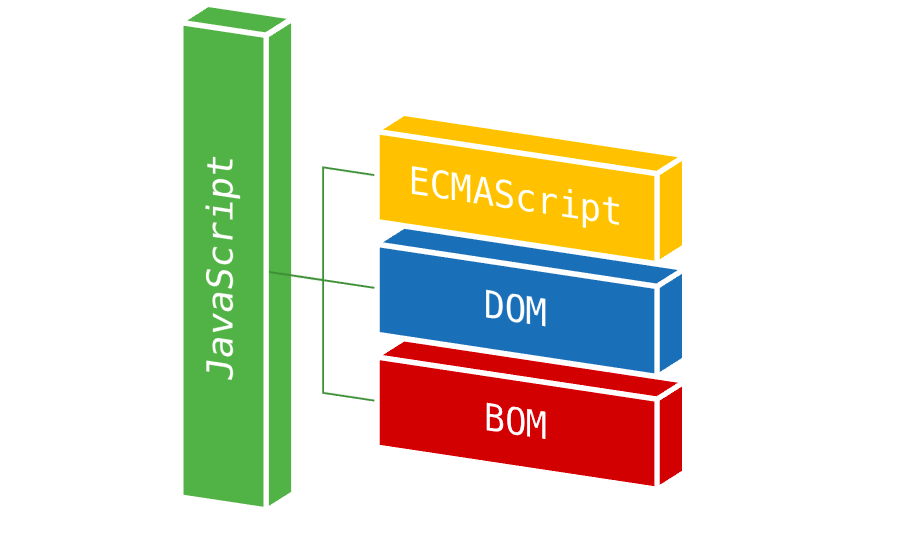
Document Object Model is a language-independent interface for work with HTML documents. It offers a set of properties and methods to search for, create and delete elements, respond to user actions, and much more. In other words, it serves as a link between the page and the programming language.
DOM is a reflection of an HTML document, a tree structure in which each node is a JavaScript object with properties and methods, a portion of the HTML document. Every element in a document, the entire document, a heading, link or paragraph are parts of this document’s DOM, so they can all be changed from JavaScript code.
Browser Object Model is a language-independent interface for work with browser tabs. It offers a set of properties and methods to access directly the current tab and a number of browser functions. This model includes an object to work with navigation history, location, and more.
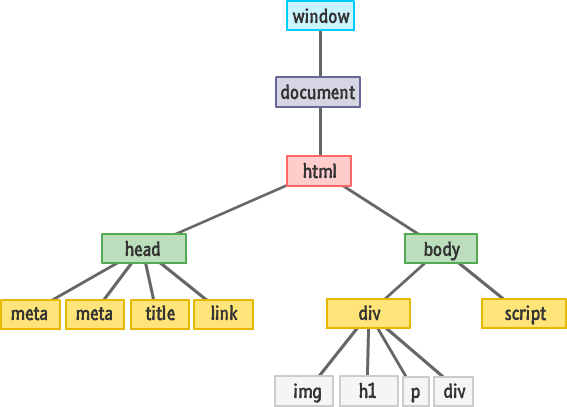
HTML document and DOM
According to the DOM model, each tag forms a separate node element, whereas each piece of text is a text element. An HTML document is a hierarchical tree in which every element (except for the root) has only one parent, that is, the element within which it is located. This tree is formed by the nested structure of tags and text elements.
To display an HTML document, the browser first converts it to a format it understands, DOM. Browser engines have a special piece of code called an HTML parser that is used to convert HTML to DOM.
In HTML, nesting defines a parent-child relationship between elements. In DOM, objects are linked in a tree-like data structure that consolidates these relationships.
The browser builds DOM gradually; as soon as it gets the first pieces of code, it starts parsing HTML, adding nodes to the tree structure.
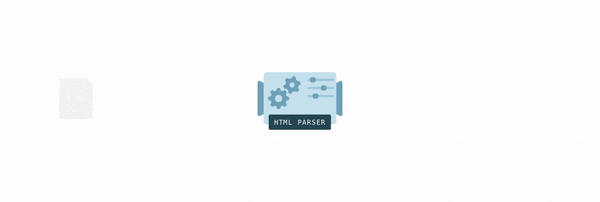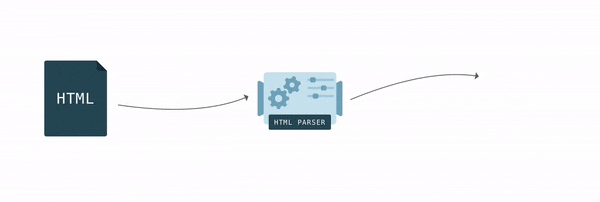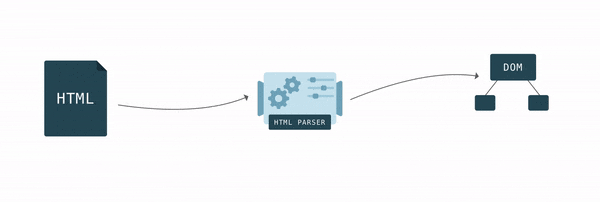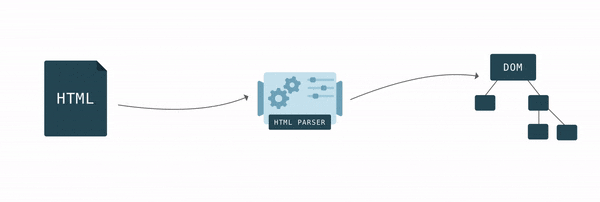
After the DOM tree is ready, you can find elements using JavaScript and perform some actions with them, since each element has an interface with many properties and methods.
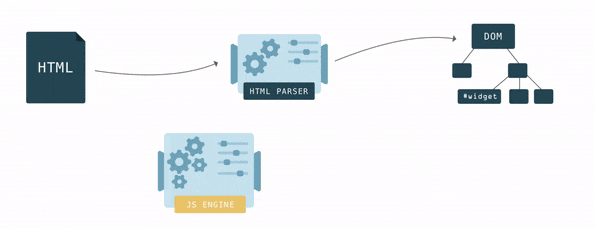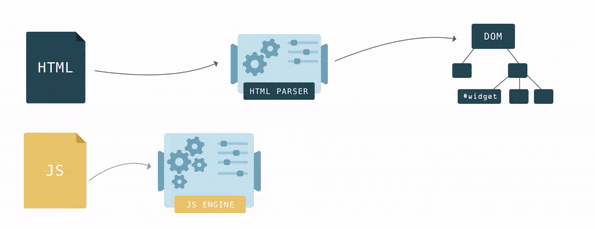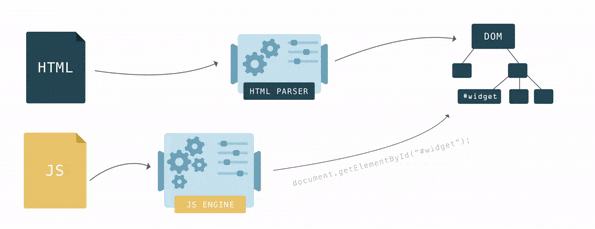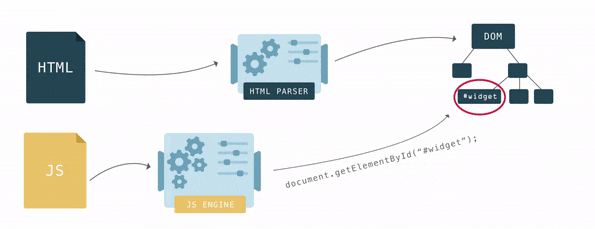
DOM tree
Let’s view the tree of an HTML document using the DOM tree generator service.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Document title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Page title</h1>
<ul>
<li><a href="#">Link 1</a></li>
<li><a href="#">Link 2</a></li>
</ul>
</body>
</html>
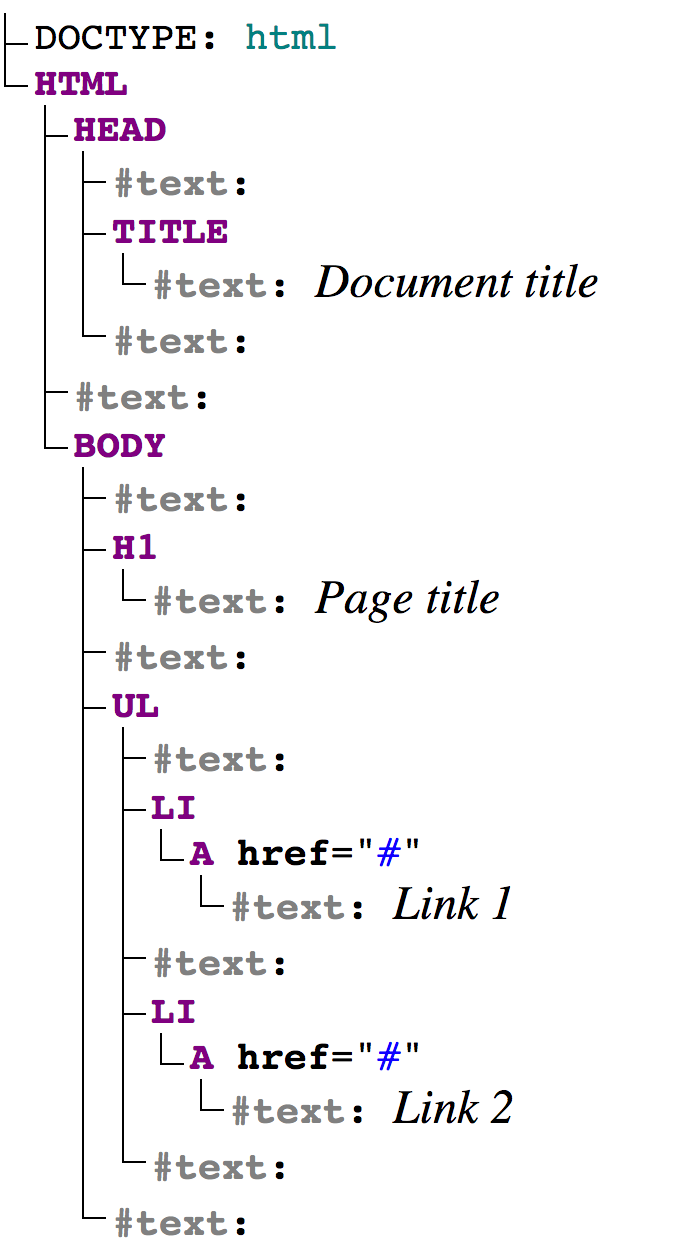
This tree has two types of nodes.
- Element nodes formed by tags, as naturally some elements are nested within others. The tree structure is formed solely by them.
- Text nodes formed by text inside elements. A text node contains only a line of text and cannot have descendants, that is, it always stays at the lowest hierarchy level. Spaces and line breaks are also text nodes.
There are exceptions to this rule: spaces before head are ignored, and any content after body does not create an element; the browser moves it to the end of body.