DOM Traversal
DOM offers many possibilities to work with elements and their content, but to
use it, you first need to get a reference to it. Access to DOM begins with the
document object, from which you can access any elements.
document is part of the global window object that is available in the script
when executed by the browser. The same as alert, console.log, prompt and
many others.
DOM tree elements are hierarchically related to each other. Such terms as ancestor, descendant, parent, child and sibling are used to describe their relationships.
- The topmost element is called a root node.
- Each element, except for the root, has only one parent.
- Elements can have any number of children.
- Siblings are elements that share the same parent.
- Children are elements nested directly inside the current one (first nesting).
- Descendants are all the elements nested inside the current one, together with their children, the children of their children, etc, i.e. the entire subtree.
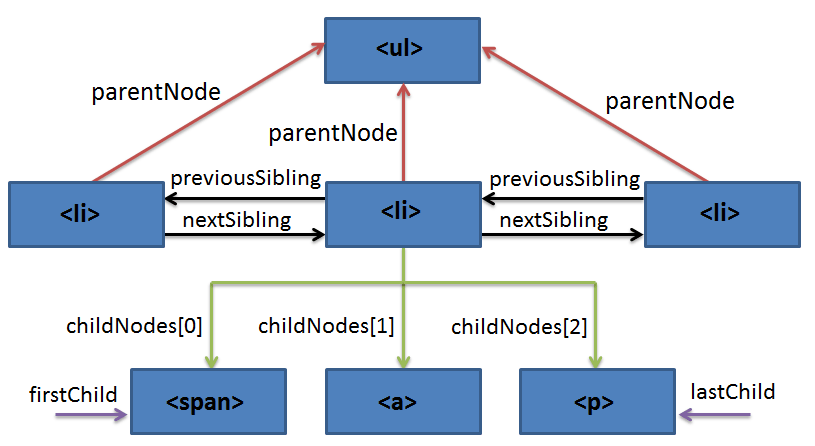
To navigate this hierarchy, use the following elements properties:
elem.parentNodeselects the parent ofelem.elem.childNodesis a pseudo-array that stores all child elements, including text ones.elem.childrenis a pseudo-array that stores only child element nodes, that is, corresponding to tags.elem.firstChildselects the first child element insideelem, including text nodes.elem.firstElementChildselects the first child element node insideelem.elem.lastChildselects the last child element insideelem, including text nodes.elem.lastElementChildselects the last child element node insideelem.elem.previousSiblingselects the element to the left ofelem(its previous sibling).elem.previousElementSiblingselects the element node to the left ofelem(its previous sibling).elem.nextSiblingselects the element to the right ofelem(its next sibling).elem.nextElementSiblingselects the element node to the right ofelem(its next sibling).
Open this example in a separate window and see the logs in the developer console.
DOM collections such as childNodes and children are pseudo-arrays
(NodeList); they do not have most of the array methods.