HTTP Protocol
Before users see the content of a website on their computer screens, the browser makes a request to the server to get this very content. HTML files, images, styles and scripts come from the server via the HTTP protocol, a set of rules and conventions used for transferring data over the web.

HyperText Transfer Protocol is a popular protocol for transferring various types of web resources: html, css, javascript, images, audio and video, etc.
HTTP is based on the client-server structure and the request-response model, in which the client application initiates a connection, generates a request and sends it to the server, after which the server processes this request, generates a response and sends it back to the client. They communicate through a series of alternating HTTP requests and HTTP responses.

The request goes through several stages:
- DNS query is looking for the nearest DNS server to convert the domain name (for example
google.com) into its numeric representation, IP address (74.125.87.99). - Connection is establishing a connection to the server using the received IP address.
- Sending data is sending packets from the client to the server.
- Waiting for response is waiting for the data packets to reach the server, after which it will process them and return a response.
- Receiving data means that the packets are here, and you can retrieve data from them.
HTTPS protocol
HyperText Transfer Protocol Secure is an extension of the HTTP protocol in which all messages between the client and the server are encrypted to improve security. It provides protection against eavesdropping attacks. Data is transferred over SSL or TLS cryptographic protocols.
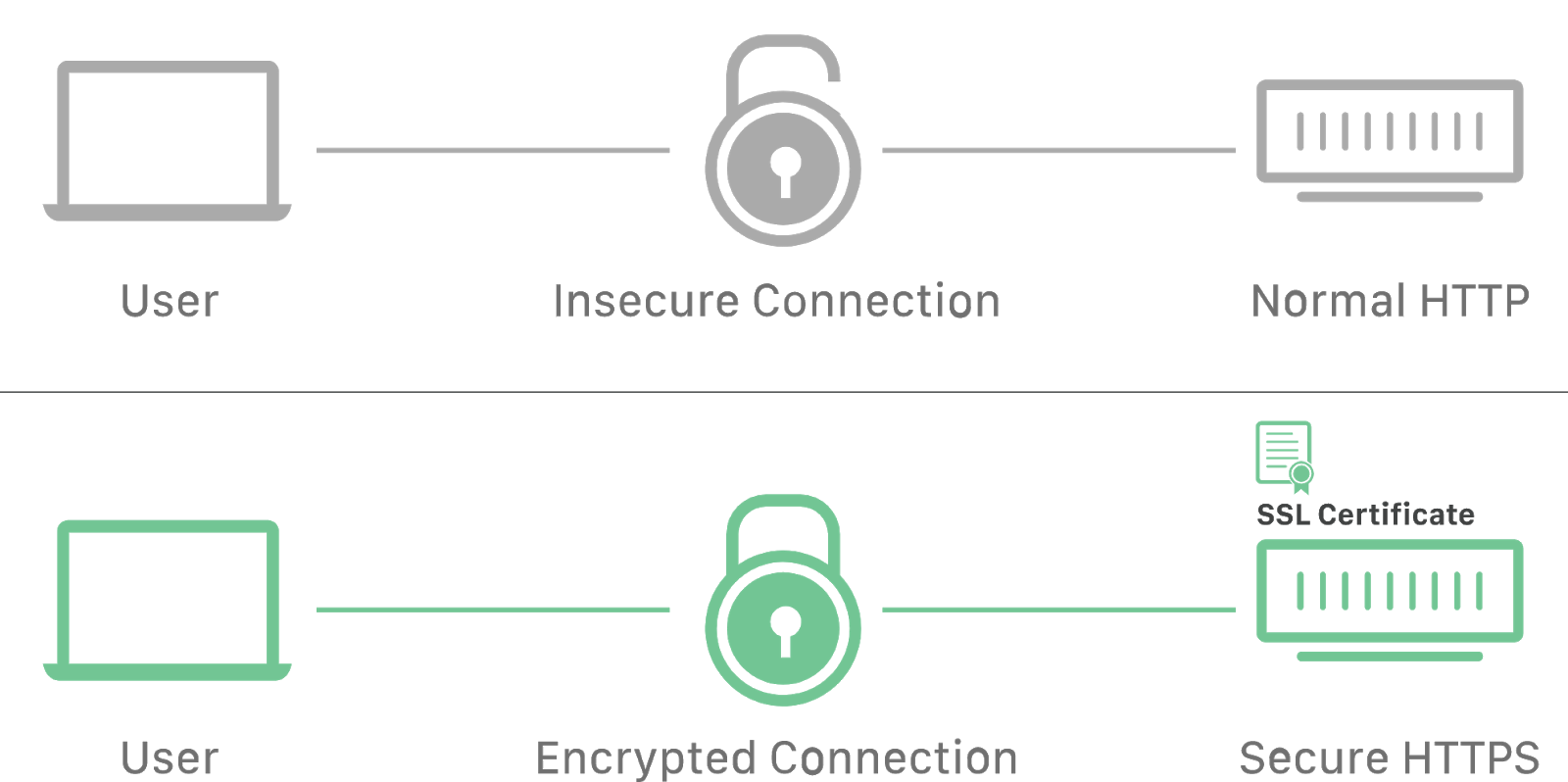
When communicating over a standard HTTP connection, all data is transferred in the text form and can be read by anyone who has gained access to the connection between the client and the server. When users shop online and fill out order forms containing credit card information, their financial data is much easier to steal if it is transferred as text. With HTTPS, the data will be encrypted and hackers will not be able to decrypt it, because decryption requires access to the private key that is stored on the server.
The HTTPS protocol ensures that customer information, such as credit card numbers, is encrypted and cannot be eavesdropped in decrypted form. Visitors can make sure that the site is safe by looking at the icon to the left of the address bar, as secured connections are marked with a padlock icon.