Call Stack
When a function is called, other functions can be called inside its body, and still other inside them, etc. JavaScript is a single-threaded language, that is, only one statement can be executed at a time. This means that the functions that have been called but not yet finished their execution, in order to continue their work, must wait for the functions called inside them to be executed.
function fnA() {
console.log("Log inside fnA function before calling fnB");
fnB();
console.log("Log inside fnA function after calling fnB");
}
function fnB() {
console.log("Log inside fnB function");
}
console.log("Log before calling fnA");
fnA();
console.log("Log after calling fnA");
// "Log before calling fnA"
// "Log inside fnA function before calling fnB"
// "Log inside fnB function"
// "Log inside fnA function after calling fnB"
// "Log after calling fnA"
You need a mechanism for storing a list of functions that have been called but have not yet finished their execution, and a mechanism for managing the execution order of these functions, which is done by a call stack.
Stack
Stack is a data structure using the LIFO (Last-In-First-Out) principle. The last thing that is added to the stack will be removed from it first, which means that you can add or remove elements only from the top of the stack.
Think of a stack as an array that only has pop and push methods, i.e. you can add or remove only the last element of the collection.
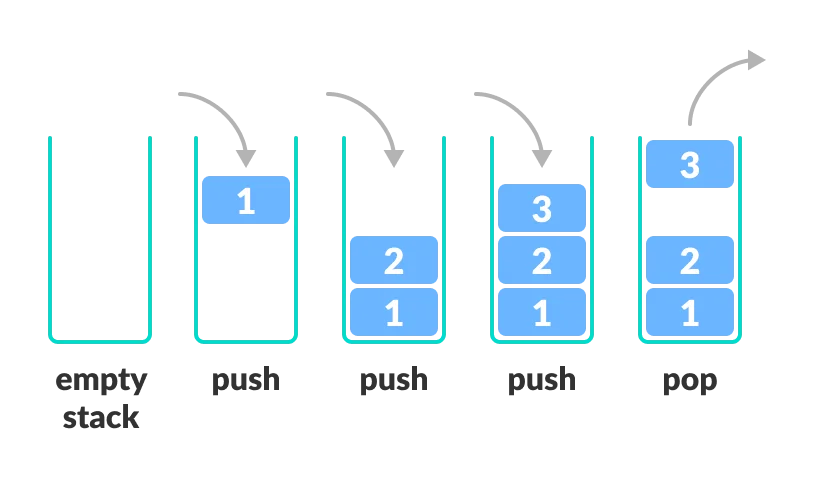
Call stack
Call stack is a mechanism for keeping track of where the interpreter is located in the code that calls multiple functions. You can see which of the functions is currently being executed, which functions are called from within the function being executed, which will be called next, etc.
- When a script calls a function, the interpreter adds it to the call stack and starts execution.
- Any functions called by the function being executed are added to the call stack and executed as soon as they are called.
- When the execution of the function is completed, the interpreter removes it from the call stack and resumes code execution from the last interruption point. That is, it starts executing the next function on the stack.
Stack frame is a structure that is added to the stack when the function is called. It stores information such as the function name and the line number in which the call occurs.
function bar() {
console.log("bar");
}
function baz() {
console.log("baz");
}
function foo() {
console.log("foo");
bar();
baz();
}
foo();
When executing this code, first foo() is called, then bar() is called inside foo(), and then baz(). Calling console.log() also counts because this is a function. The illustration below shows a call stack example.
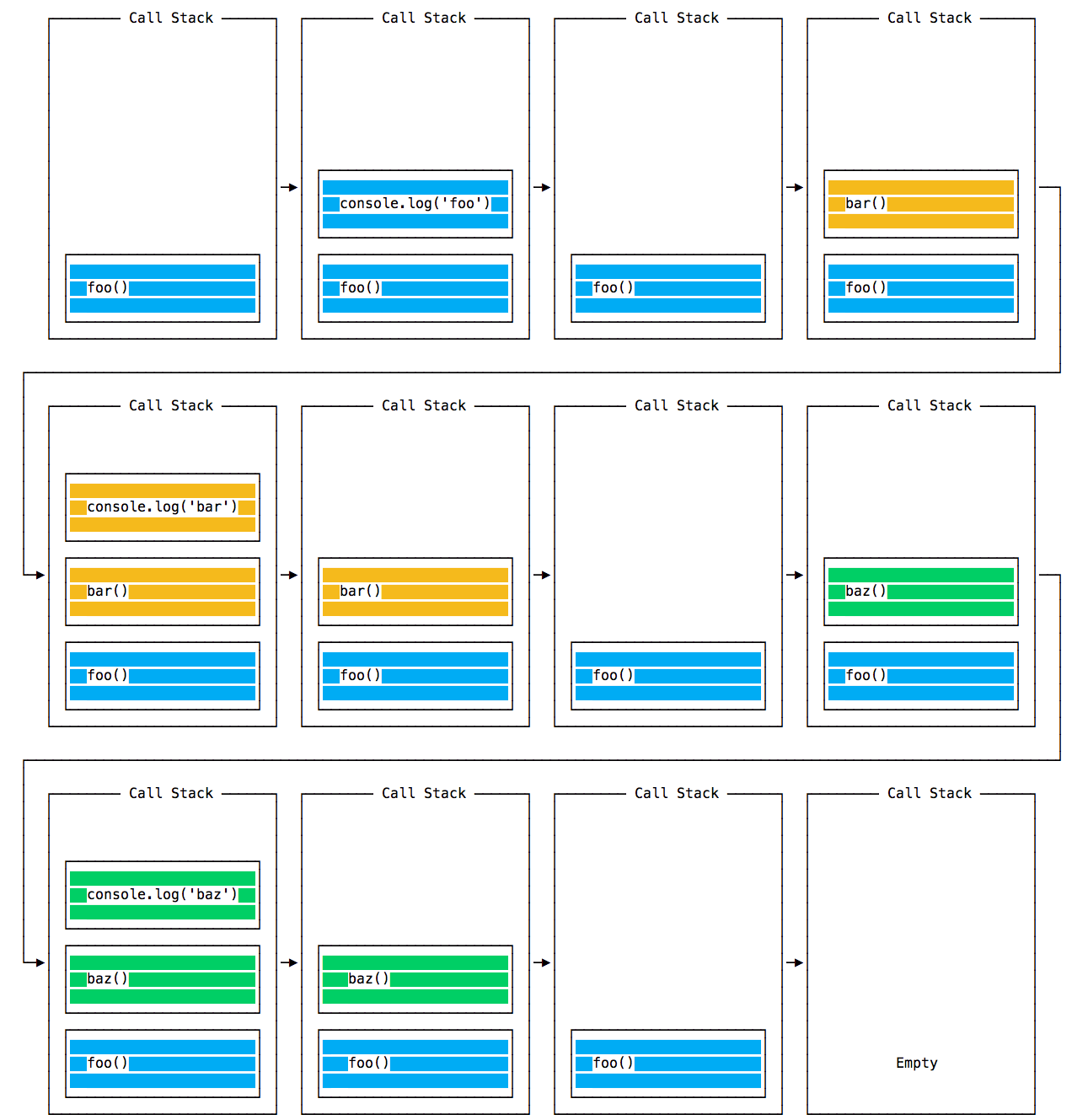
Call stack overflow
The call stack is not limitless, it is allocated a finite amount of memory. Sometimes in the console you can see the error "Uncaught RangeError: Maximum call stack size exceeded", i.e. stack overflow.
This can happen due to improper use of recursion or looping of function calls, that is, when there are infinite function calls and no result is returned, then the stack grows. Upon reaching the stack size limit, you will see this error message, with your script "crashing".